Throat Cancer
- Introduction
- Where Does Oral Cancer Develop?
- Types of Throat Cancer
- Causes of Throat Cancer
- Symptoms of Throat Cancer
- What are the stages involved in the growth of Throat Cancer?
- How can you prevent Throat Cancer?
- Throat Cancer Post-treatment Recovery
- How Punarjan Ayurveda Treats Oral Cancer?
- Our Oral Cancer Survivor Stories
- FAQ’s
In a world where our words hold immense power, it is crucial to recognize the importance of oral health. Behind the captivating smiles and animated conversations lies a lesser-known threat lurking in the shadows: oral cancer. This silent menace can mar the essence of our communication and put our lives at risk.
The lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, floor of the mouth and roof of the mouth are all potential sites of oral cancer, often known as mouth cancer. It typically begins as an unassuming sore or ulcer, often painless, which can easily go unnoticed in the early stages. However, oral cancer can become life-threatening as it progresses, spreading to nearby tissues and potentially metastasizing to other body parts.
In India, 78,000 new cases of oral cancer are diagnosed annually, accounting for around 3% of all cancer diagnoses.
Those above 40 have an increased risk of developing mouth cancer; men are more than twice as likely to have it than women. Tobacco usage, alcohol consumption, or HPV infection are the leading causes of oral cancer.
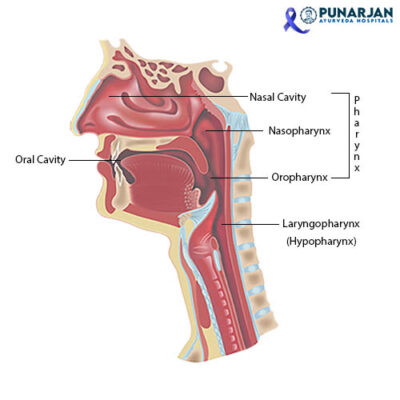
Where Does Oral Cancer Develop?
Several parts of the mouth and throat are at risk for developing oral cancer. In most cases, dentists are the first medical professionals to notice oral cancer.
- Lips: The outer or inner surface of the lips can be a site for developing oral cancer.
- Tongue: Oral cancer can affect both the front (oral tongue) and back (base of tongue) parts of the tongue. The latter is often associated with human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.
- Gums: The tissues surrounding the teeth, known as the gums or gingiva, can be susceptible to oral cancer, especially in individuals with poor oral hygiene or chronic irritation from dentures or tobacco use.
- The floor of the mouth: This refers to the area beneath the tongue, where the mouth floor meets the lower jaw.
- Palate: The roof of the mouth, consisting of the hard palate (bony front portion) and the soft palate (muscular back portion), can be affected by oral cancer.
Salivary glands: Although less common, oral cancer can also originate in the salivary glands, which produce saliva. These glands are located in various areas around the mouth and throat.
Early Prevention through Ayurveda:
Ayurvedic treatment for throat cancer may involve a combination of herbal remedies, dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and other therapies. Below is a small list of some of the ayurvedic herbs and easy remedies that may be used to treat throat cancer.
Tulsi or Holy Basil: Tulsi is a very powerful antioxidant that has been found to have anti-cancer properties. It helps prevent the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Turmeric: We know that turmeric is a spice that has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for thousands of years. Because it contains a compound called curcumin (which has anti-cancer properties).

Amla or Indian Gooseberry: It is important to know that this regular Amla is a rich source of antioxidants and vitamin C. It can boost the immune system and prevent the growth of cancer cells.
Ashwagandha: It is an adaptogenic herb that may help reduce stress and improve your overall health. It improves the effectiveness of cancer treatments.
Yoga: Ayurveda, in the first place puts a strong emphasis on mental and emotional well-being. Hence, Yoga and meditation are crucial to reduce stress and improve overall health.
Types-Of-Oral-Cancer
SCC
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the standard oral cancer. Squamous cells line the mouth, tongue, and lips, and this is where it all starts.
Verrucous carcinoma is an uncommon kind of SCC. In most cases, it stays localized. However, it can potentially spread into the deeper layers of mouth tissue. Over the past 30 years, the reported incidence of SCC has risen by as much as 200 percent.
BCC
More than 75 out of every 100 occurrences of skin cancer are basal cell carcinomas.
The lower epidermis, which contains the basal cells, is where it begins to form. Lips are just another sun-exposed body part where BCC can develop.
Salivary gland cancer
There are several salivary glands in and around the mouth. Most salivary gland tumors are benign. But occasionally, cancer can form there. Adenocarcinomas, which form in glandular tissue, account for most of these tumors.
The parotid glands in the cheeks are a possible origin point for cancer of the salivary glands. They may also begin in the glands under the tongue and jaw.
Oral precancerous lesions
Certain conditions, such as leukoplakia (white patches) or erythroplakia (red patches), can indicate a higher risk of developing oral cancer.
Adenoid cystic tumors
This is an uncommon type of cancer. These tumors can develop in the glandular tissue in the mouth’s salivary glands, usually in the parotid glands. They can also develop in the breast, skin, cervix, prostate, and other areas.
Lymphoma
The spleen, tonsils, thymus gland, and other glands in the body are all part of the lymphatic system, so that lymphoma can affect any part of the body.
Although relatively rare, lymphomas can develop in the oral cavity, affecting lymphatic tissues and immune cells.
Melanoma
Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm that originates in the melanin-producing skin cells. This type of oral cancer is quite rare. However, because of how rapidly it multiplies and spreads, it poses a special hazard.
HPV-positive cancer
Young people with no history of cigarette or alcohol use are disproportionately affected by HPV-positive cancer, a less prevalent form of mouth cancer.
Causes For Oral Cancer
Alcohol and drug abuse
People who smoke have a higher risk of developing oral cancer, especially cigarettes. Risk factors can include heavy alcohol consumption. Adding alcohol to cigarette use significantly raises the danger level.
HPV
Oral malignancies have been associated with infection with certain types of sexually transmitted human papillomavirus, most notably HPV 16. HPV is primarily transmitted through sexual contact.
Age
The danger grows as one age. People over 40 have an increased risk of developing oral cancer.

Sun Exposure
Prolonged and excessive exposure to sunlight can increase the risk of lip cancer, a type of oral cancer that affects the lips.
Weakened Immune System
Oral cancer is more likely in people with compromised immune systems, such as HIV/AIDS or organ transplant recipients on immunosuppressive medicines.
Betel Quid
Chewing betel quid, a mixture of betel leaf, areca nut, and other ingredients, is prevalent in some parts of Asia and strongly linked to an increased risk of oral cancer.
What Are The Complications of Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer and its treatment can potentially cause some unpleasant side effects. There is a chance of complications like:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Pain
- Trouble eating and swallowing after surgery.
Long-term problems may include the following:
Narrowing of the carotid artery: Radiation therapy has the potential to cause this side effect, which can then progress to cardiovascular issues.
Dental problems: Issues with teeth and gums might arise if the jaw or mouth is altered surgically.
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing: Difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia, can make eating a challenge and raise the risk of inhaling food, which can lead to bacterial and viral illnesses.
Speech problems: Alterations to the lips, tongue, and jaw might cause difficulties pronouncing words.Mental health issues: Depression, impatience, irritation, and worry are all signs of a mental health problem.
Symptoms Of Oral Cancer
Lips, gums, and even the throat are not off-limits for the progression of mouth cancer.
These are the most typical warning signs of oral cancer:
- A persistent lip or mouth ulcer.
- A tumor or tumor in your mouth.
- Experiencing oral bleeding.
- Tooth decay, Discomfort, or trouble swallowing.
- Difficulty with Dentures Painful nodule in the neck.
- Constant pain in one’s ear.
- Extreme weight reduction.
- Lip, cheek, and chin numbness; sometimes extends to the neck.
- Discolored areas of the mouth or lips can be white, red, or a combination.
- Throat pain.
- Tightness or Discomfort in the jaw.
- Pain in the tongue.
Other symptoms may include:
- Discomfort or dysphagia (swallowing trouble).
- Modifications to your voice or difficulties communicating.
- Loss of weight without trying Discoloration or bleeding of the gums.
- Experiencing one or more teeth going loose without apparent cause or a tooth socket that does not heal after an extraction.
- Tougher-than-usual jaw movement.
- Red or white bumps inside the mouth.
These are frequent and usually don’t indicate cancer, but they can develop into cancer, so it’s best to be checked out if you notice any of these symptoms.

What Are The Stages Involved In The Growth Of Oral Cancer?
The stage of cancer can be identified with the aid of diagnostic testing. If the cancer has spread or gone behind the skin, its location is described by its stage. The spread of cancer to other organs is also investigated through testing.
Doctors use information about the disease’s stage to provide therapy suggestions and prognoses. Oral cancers are categorized using the TNM staging method.
T denotes the primary tumor’s extent and location. If your tumor has migrated to your lymph nodes, you will see an N. Metastasis, denoted by the letter; M, which means the tumor has spread to other body parts.
The stages of oral cavity cancer are:
- TI: Your oral tumor is no more than 2 centimeters in diameter.
- T2: The size of the tumor is between 2 and 4 centimeters.
- T3: The size of the tumor is greater than 4 centimeters.
- T4: Cancer cells have spread from the primary tumor to neighboring tissues, lymph nodes, or other organs.
The National Cancer Institute is a reliable source when it comes to information on malignancies of the mouth and throat:
- 83% for non-spread localized cancer
- 65% for cancer that has progressed to surrounding lymph nodes
- Cancer that has spread to other regions of the body is 38%
Sixty percent of those diagnosed with mouth cancer will be alive after five years. The likelihood of recovery after treatment improves with earlier stages of diagnosis. Stage 1 and 2 oral cancer patients had a 70-90% five-year survival rate. This emphasizes the significance of prompt diagnosis and treatment.

ORAL CANCER STAGING SYSTEM
The best course of treatment is determined only after a precise cancer diagnosis. First, a leading oncologist in India will examine the growth and determine the cancer’s progression.
An optimal treatment strategy is developed depending on the cancer’s stage. The American Joint Committee’s TNM method is commonly used for staging oral cancer. The three main pillars of this widely acknowledged technique for cancer staging are:
- T (Tumour)- This defines the original size of the tumor when it was diagnosed.
- N (Node)- This straightforward metric can reveal whether or not the malignancy has progressed to the lymph nodes in the affected area.
- M (Metastasis)- This represents whether cancer has spread to other body parts.
In addition to these three standards, a number value ranging from 0 to 4 is ascribed to each constituent. A larger numerical value indicates a greater degree of that component. A tumor of the T1 stage is less advanced than one of the T4 stage. An ‘X’ may be used when further evaluation of a given item is impossible.
How Can You Prevent Oral Cancer?
Scientists believe that damage to the DNA of cells in the mouth is the initial step in developing oral cancer. However, your health practices, among other factors, can increase your risk.
Different types, locations, and stages of oral cancer require different treatment approaches.
Surgery
Surgical removal of the tumor and any lymph nodes impacted by the malignancy is the therapy of choice for cancer in its earlier stages. Tissue from the neck and mouth area may also be removed.

Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are typically combined to treat patients whose cancer has progressed to an advanced stage. There is also the possibility of radiation therapy. Radiation beams are directed towards the tumor by a doctor once or twice per day, five days per week, for two to eight weeks as part of this treatment.
Chemotherapy
The use of pharmaceuticals in the fight against cancer is known as chemotherapy. You can choose to take the drug orally or have it given to you intravenously. Most patients can receive chemotherapy without being hospitalized.
Targeted therapy
Treatment options also include targeted therapies. Drugs used in targeted therapy are designed to connect to specific proteins in cancer cells and stop their proliferation. It can potentially be useful for cancer patients at any stage.
Nutrition
Taking care of your nutritional needs during treatment for oral cancer is crucial. Many therapies cause Discomfort when eating or swallowing, leading to decreased hunger and possible weight loss.
By consulting a nutritionist, you can get the calories, vitamins, and minerals your body needs to recover from your illness while still eating easy foods on your tongue and throat.
Keeping your mouth healthy
Last, taking care of your mouth during cancer treatment is important. Maintain a clean and moist mouth by drinking plenty of water.
How Punarjan Ayurveda Treats Oral Cancer?
For cancer patients today, we represent a promise. Hundreds of our success stories are a beacon of hope for those seeking cancer therapy. We offer a comprehensive and distinctive treatment strategy for Oral Cancer. In fact, the human body can heal itself. It can also find equilibrium again.
An adept Ayurvedic physician should treat the underlying cause of cancer rather than only its symptoms.
Thus, it is our method of treatment in which we boost natural immunity to combat malignant cells. The patient must undergo a combination of dietary adjustments and herbal medications in order to treat oral cancer. In developing each patient’s unique treatment plan, we first take into account the patient’s health and cancer stage. Yet Punarjan Ayurveda’s approach goes beyond the physical. In the modern world, we are aware of the psychological toll that bone cancer can have on patients. We are here to provide steadfast support and guidance throughout this cancer treatment endeavor because this is a holistic approach.
According to Indian Ayurveda, people are capable of actively taking part in their own treatment. We monitor our progress, promote openness and collaboration, and work together to reach positive conclusions. Punarjan Ayurveda is a method that places a strong emphasis on individualized care, Ayurvedic wisdom, and a supportive community. It has more than two decades of research and almost a decade of cumulative success.
“Join our journey into a cancer free world”
Our Oral Cancer Survivor Stories
FAQ’s
Who is most affected by oral cancer?
Oral cancer most commonly affects:
Older Individuals: The risk increases with age; most cases occur in people over 40.
Men: Men are twice as likely to develop oral cancer, although the gap is decreasing.
Tobacco and Alcohol Users: The risk is significantly higher for smokers and alcohol consumers, especially those who do both.
Residents of South Asia: Particularly in India, due to the prevalent use of chewable tobacco products.
How long does oral cancer take to form?
The exact timeline for the development of oral cancer can vary greatly, but it typically develops over several years. It often begins as a small, unnoticed spot or sore in the mouth that gradually grows and spreads. Although it can manifest at any age, oral cancer is frequently diagnosed in individuals above 40. Early signs of oral cancer can be detected through regular dental check-ups, potentially leading to life-saving outcomes.
Is oral cancer easy to treat?
Yes, early detection renders treatment more manageable. The American Cancer Society estimates that the 5-year survival rate for localized oral and oropharyngeal cancer (where cancer remains confined to the primary site) stands at 84%.
Nonetheless, the survival rate experiences a notable decline once cancer spreads to neighboring tissues, organs, and/or regional lymph nodes. The 5-year survival rate for regional and distant stage diagnoses are 66% and 39%, respectively.
Is oral cancer genetic?
Yes, oral cancer may involve a genetic aspect. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that environmental and lifestyle elements, such as tobacco usage, excessive alcohol consumption, and specific types of human papillomavirus (HPV), substantially increase the risk.
How can we prevent oral cancer?
Preventing oral cancer primarily involves lifestyle modifications:
Avoid Tobacco: All forms of tobacco can cause oral cancer. Avoidance is crucial.
Limit Alcohol: Excessive alcohol is a risk factor. Limit intake to moderate levels.
Nutritious Diet: Incorporating ample fruits and vegetables into your diet is a preventive measure against oral cancer.
Routine Examinations: Consistent dental check-ups play a crucial role in early detection.
Solar Safeguard: Shield your lips from the sun’s rays to minimize the risk of lip cancer.
HPV Inoculation: Getting vaccinated against HPV can forestall HPV-associated oral cancers.
Which food is good for oral cancer?
A balanced diet is crucial for oral cancer prevention and management. Key food recommendations include:
Fruits and Vegetables: Abundant in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, they impart a robust immune system and thwart damage from unsafe free radicals.
Flavonoids: Present in berries, apples, citrus fruits, and onions, flavonoids boast antioxidant characteristics that can diminish the peril of oral cancer.
Lean Proteins: Fish, poultry, and tofu, among others, furnish indispensable proteins essential for cell repair and growth.
Whole Grains: Whole grain bread, brown rice, and oatmeal, constituting foods high in fiber, facilitate digestion and can potentially aid in cancer prevention.
Limiting alcohol and abstaining from tobacco are also pivotal, as they are recognized risk factors for oral cancer.
Limiting alcohol and avoiding tobacco is also crucial as they are known risk factors for oral cancer.
What is the success rate of oral cancer?
The success rate for oral cancer displays considerable variation, primarily reliant on the stage of diagnosis and global location. The prospect of successful treatment notably enhances with early detection. Nevertheless, the American Cancer Society reports an approximate 5-year survival rate of 65% for oral cancer.

